This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Different Power Gains
Types of power gain
If you hear the word 'power gain', you justly interpret this as the ratio of the output power $P_{out}$ to the input power $P_{in}$:
$$ gain=\frac{P_{out}}{P_{in}}$$
Unfortunately, confusion is possible, since there are different ways to define the ouput and input power. And depending on which definition of power you use, you get another value for the gain. But mankind has found a solution: we use different names for the gains, depending on which power is considered. Let us try to give an overview of the three most common gains.
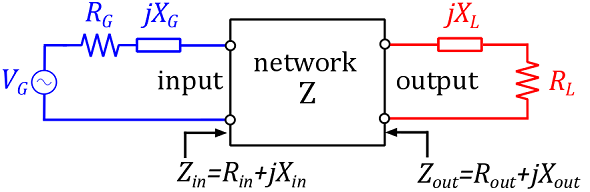
A two-port network, connected to a source and a load.
Consider a network $Z$ with one input and one output (a two-port network). The input is connected to a generator (a voltage source $V_G$ with internal impedance $Z_G=R_G+j.X_G$) and the output to a load impedance $Z_L=R_L+j.X_L$.
- We call the input impedance of the network $Z_{in}=R_{in}+j.X_{in}$. Note that the input impedance $Z_{in}$ is dependent on $Z_L$ (see figure 1).
- We call the output impedance $Z_{out}=R_{out}+j.X_{out}$. Note that the output impedance $Z_{in}$ is dependent on $Z_G$ (see figure 1).
Figure 1: A network Z is connected to a generator at the input, and a load at the output
We will define three different types of gain for the network Z. We first start by considering two different definitions of input power.